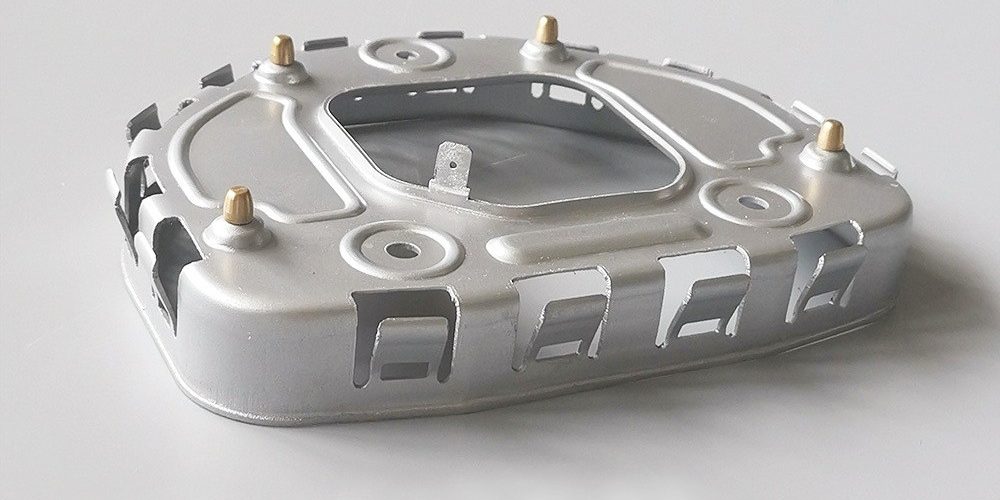
The production of sheet metal parts generally includes the following main processes:
I. Cutting
- Shearing cutting: Use a shearing machine to cut metal sheets according to the design size. It is suitable for thinner sheets.
- Laser cutting: Irradiate the metal sheet with a high-energy laser beam to melt and vaporize it to cut out the required shape. It has high precision and fast speed and can cut complex shapes.
II. Forming
- Bending: Use a bending machine to bend the sheet to form a specific angle and shape. According to design requirements, multiple bending operations can be performed.
- Stamping: Use stamping dies to stamp and form the sheet to create various concave and convex features such as holes, grooves, and bosses.
III. Welding
- Manual arc welding: Melt the metal by the arc heat generated between the electrode and the workpiece for welding. It is suitable for various metal materials, but the welding quality is greatly affected by the welder’s technical level.
- Gas shielded welding: Use shielding gas (such as carbon dioxide, argon, etc.) to prevent oxidation in the welding area. It has high welding efficiency and good quality.
- Spot welding: Mainly used for the connection of thin plates. Apply pressure and pass electricity through the electrode to the sheet to locally melt the contact point and form a welding spot.
IV. Surface treatment
- Powder coating: Attach powder coatings to the surface of sheet metal parts by electrostatic spraying. Then, after heating and curing, a uniform coating is formed, which has good anti-corrosion and decorative effects.
- Galvanizing: It can be divided into hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing. Hot-dip galvanizing immerses sheet metal parts in molten zinc liquid to form a zinc layer on the surface, with good anti-corrosion performance. Electro-galvanizing deposits a zinc layer on the surface through electrolysis, and the appearance is relatively bright.
- Polishing: Polish the surface of sheet metal parts to improve the surface finish and make it more beautiful.
V. Assembly
Assemble the various sheet metal parts according to the design requirements, usually using methods such as bolt connection and riveting. During the assembly process, it is necessary to ensure the dimensional accuracy and positional accuracy of each part to ensure the overall quality of the product.
Assemble the various sheet metal parts according to the design requirements, usually using methods such as bolt connection and riveting. During the assembly process, it is necessary to ensure the dimensional accuracy and positional accuracy of each part to ensure the overall quality of the product.
VI. Inspection
Inspect the completed sheet metal parts, including inspections of dimensional accuracy, appearance quality, welding strength, and other aspects. Only after passing the inspection can they be packaged and put into storage or delivered for use.
Inspect the completed sheet metal parts, including inspections of dimensional accuracy, appearance quality, welding strength, and other aspects. Only after passing the inspection can they be packaged and put into storage or delivered for use.